Welcome to Pedras' Lab
Chemical Ecology & Natural Products Chemistry:
Discovering Sustainable Plant Disease Treatments
Despite extensive use of fungicides, insecticides, and herbicides, plant diseases and pests continue to cause enormous yield losses worldwide. Yet, the increasing demand for food requires substantial increases in the production of staple crops. At the same time, environmental issues stress that sustainable agricultural practices cannot rely on the continuous application of pesticides. For this reason, there is an urgency to fully understand both our agricultural and natural ecosystems. This understanding requires a concerted multidisciplinary effort, which demands a multidisciplinary approach. In particular, application of chemical ecology to understand the multiple chemical interactions among various organisms is central to the discovery of safer agricultural practices and indeeduniversally sustainable crop production.
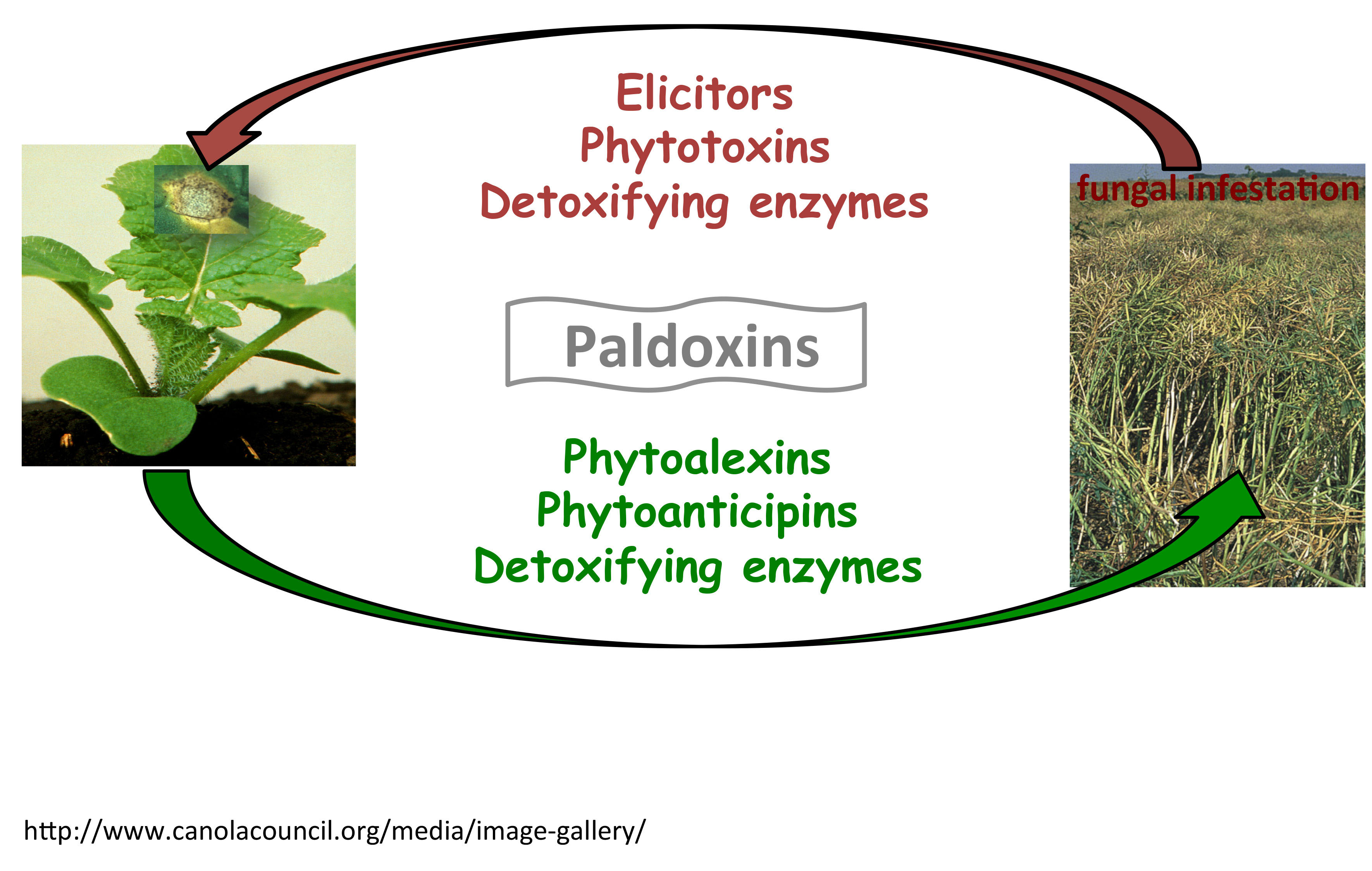
In our group we are using bioorganic, biochemical and biological techniques to understand economically important diseases of crucifers, namelyoilseeds such as canola, rapeseed, and mustard, vegetables such asrutabaga, broccoli, and turnip, and condiments such as radish andwasabi. In addition, a particular effort to discover wild species displaying unique defense pathways is underway. We are focusing on the interactions of these plants with significant fungal pathogens such as blackleg, black spot, root rot, stem rot, grey mould and white rust (Figure 1). Experimental work combines a wide variety of chemical and biological studies including:
- chemical structure determination of bioactive metabolites synthesized by pathogens (e.g. phytotoxins and elicitors) and plants (e.g. phytoalexins and phytoanticipins) with development of bioassays;
- biosynthesis and metabolism of these bioactive compounds in pathogens and plants;
- chemical synthesis of bioactive compounds and intermediates/products of detoxification pathways;
- isolation and characterization of detoxifying enzymes;
- design of inhibitors: paldoxins (inhibitors of phytoalexin detoxifying enzymes) and inhibitors of phytotoxin biosynthesis.